Are you noticing a subtle increase in abdominal fat as you journey through menopause? Rest assured, this phenomenon is entirely commonplace during the hormonal shifts of this life stage, even if your daily habits remain unchanged. Let's delve into the intricate world of hormonal belly fat and what you need to be aware of as you navigate this transformative period.
Understanding the Culprits Behind Belly Fat
Weight gain, especially the accumulation of abdominal fat, is influenced by various factors. These include your daily caloric intake, physical activity levels, age, and muscle mass. As you age, muscle mass typically diminishes while fat content rises. These changes, combined with declining estrogen levels during menopause, contribute to the development of belly fat.
However, the story isn't solely about calories and hormones. Your genetic predisposition, gut microbiome, sleep patterns, daily stressors, and prior exposure to environmental toxins all play a role in the intricate tapestry of weight gain. Some factors are within your control, while others are not, leading to a complex interplay of elements contributing to weight fluctuations.
Distinguishing Hormonal Belly Fat from Normal Weight Gain
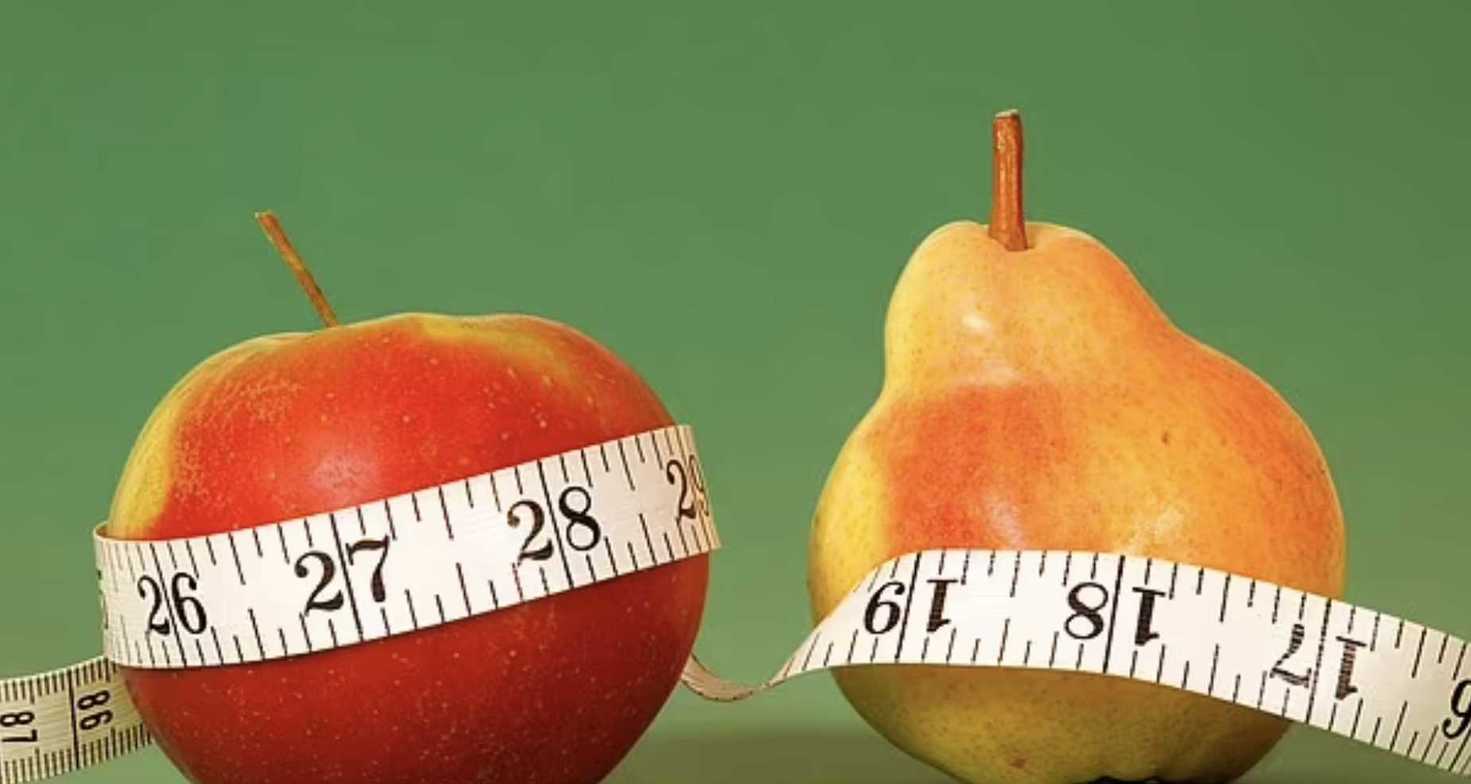
Throughout your reproductive years, many women exhibit a "pear-shaped" body, with fat distribution concentrated around the hips, buttocks, and breasts. This type of fat is subcutaneous, residing just beneath the skin.
However, after menopause, the body's shape tends to shift toward an "apple shape," characterized by the accumulation of fat around the midsection. This particular fat is referred to as visceral or abdominal fat, which lies deeper within the body, enveloping organs like the liver, stomach, and intestines.
Your genetic makeup largely dictates your body shape and visceral fat storage. Environmental factors, such as dietary choices and physical activity levels, also exert considerable influence. An unhealthy diet, featuring excessive consumption of fatty foods and carbohydrates, coupled with a sedentary lifestyle, can increase the likelihood of accumulating visceral fat.
Moreover, stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that activates the body's "fight-or-flight" response and can lead to increased storage of visceral fat.
The Role of Menopause in Triggering Hormonal Belly Fat
When it comes to belly fat, your hormonal profile takes center stage during menopause, as it initiates alterations in fat distribution. During this phase, estrogen levels experience a significant decline, representing a pivotal factor in fat distribution. Estrogen, a paramount sex hormone, is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics, including fat distribution around the breasts and waist during adolescence. As estrogen levels diminish, so do the dynamics of your body composition.
This is why estrogen and visceral fat maintain an inverse relationship: higher estrogen levels correspond to lower visceral fat, and vice versa.
Strategies to Tackle Hormonal Belly Fat
Embarking on a journey to shed excess weight can be challenging. If you're determined to transform your body shape, it's advisable to harness a comprehensive approach, working closely with your healthcare provider to ensure a holistic and successful transformation.
1. Engage in Physical Activity: Research underscores the efficacy of a multifaceted exercise routine, combining aerobic workouts, strength training, and balance exercises like yoga. This blend of exercises not only aids weight management but also provides protection against other menopausal symptoms, such as bone density loss and muscle mass decline.
2. Revamp Your Eating Habits: While the desire to lose weight may tempt you to experiment with fad diets, many of them yield unsustainable results. A notable exception is the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes whole foods like fruits, nuts, vegetables, legumes, healthy fats, and whole grains. Consuming meat, sweets, dairy, refined grains, and processed foods in moderation has been shown to facilitate weight loss and muscle preservation post-menopause.
3. Prioritize Sleep: Sleep is a cornerstone of overall health, particularly during menopause, when your body grapples with significant hormonal changes. Sleep disruptions during this period may reduce fat burning, potentially contributing to weight gain. To optimize your sleep, adhere to good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a quiet, dark bedroom, limiting screen time before bedtime, adhering to a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine in the afternoon, and reserving your bed exclusively for sleep.
4. Manage Stress: Menopause often ushers in substantial hormonal shifts that can be accompanied by heightened stress levels. Research has underscored the undeniable link between stress and weight. Mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques have shown promise in mitigating stress and enhancing sleep quality during menopause. Furthermore, incorporating stress management into weight loss programs has been demonstrated to enhance their effectiveness. Numerous mindfulness resources are available online, with meditation apps like Headspace and Calm offering convenient access to these practices.
5. Consider Hormone Therapy: Bio-identical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) employs estrogen medication to supplement diminishing natural hormone levels. It represents the gold standard for managing hot flashes, night sweats, and various other menopausal symptoms, including depression and insomnia.BHRT is the sole treatment capable of addressing the root cause of menopausal body changes—estrogen deficiency. By elevating estrogen levels, it may help counteract the visceral weight gain associated with menopause. If you're interested in BHRT make a complementary appointment with Dr. Anat Sapan on Doctoranat.com
In Conclusion
Hormonal belly fat is a common aspect of the menopausal journey, but you don't have to resign yourself to it. Embracing a holistic wellness approach, featuring sensible exercise, stress management, and sustainable dietary habits, can empower you to counteract menopausal weight gain. Additionally,Bio-identical hormone replacement therapy offers a potential solution by addressing the underlying estrogen deficiency. Remember that your healthcare provider is an invaluable partner in navigating this transformative phase, ensuring that your physical, mental, and emotional well-being are nourished along the way.

Anat Sapan, MD
Contact Me